October 24 Advisory: Zero day in Fortinet FortiManager seeing Active Exploitation [CVE-2024-47575]
Date of Disclosure: October 23, 2024
CVE-2024-47575 is an actively exploited, critical vulnerability in Fortinet FortiManager that could allow a remote unauthenticated actor to execute arbitrary code through specially crafted requests. While the NVD is still analyzing the vulnerability, Fortinet has assigned it a CVSS score of 9.8.
FortiManager is a management tool designed for controlling various FortiGate network and security appliances such as firewalls and VPNs. Threat actors often target network devices due to the insights they provide about an organization’s overall network environment and the opportunities for additional post-exploitation activities.
Mandiant has observed a new threat actor group “UNC5820” exploiting this vulnerability, in over 50 FortiManager devices since June 27, 2024, to exfiltrate configuration data from FortiGate devices. This data could enable further network compromises and lateral movement, but Mandiant has found no evidence of such activities so far. UNC5820’s motivations remain unclear, but their broad targeting across industries indicates a high level of sophistication.
Organizations with public-facing FortiManager instances should check for indicators of compromise as soon as possible. See the provided Censys queries below to help track exposures. It’s recommended to avoid the exposure of network device admin portals on the public internet.
| Field | Details |
| CVE-ID | CVE-2024-47575 – CVSS 9.8 (Critical) assigned by Fortinet |
| Vulnerability Description | Missing authentication in a critical function of FortiManager could allow unauthenticated remote code execution. |
| Date of Disclosure | October 23, 2024 |
| Affected Assets | FortiManager and FortiManager Cloud |
| Vulnerable Software Versions | FortiManager versions: 7.6.0, 7.4.0-7.4.4, 7.2.0-7.2.7, 7.0.0-7.0.12, 6.4.0-6.4.14, 6.2.0-6.2.12
FortiManager Cloud versions: 7.4.1-7.4.4, 7.2.1-7.2.7, 7.0.1-7.0.12, and all 6.4 versions |
| PoC Available? | No, at the time of writing |
| Exploitation Status | There has been active exploitation by a threat group tracked as “UNC5820.” CISA has added this to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog. |
| Patch Status | Patches are available for all affected devices, as well as workarounds. See Fortinet’s vendor advisory for instructions. |
Censys Perspective
At the time of writing, Censys observed 4,081 exposed FortiManager admin portals online, with about 30% concentrated in the United States. Censys observed about 20% of the exposed instances to be associated with Microsoft Cloud (ASN 8075). About 86% were exposed via the default FGFM management port, TCP port 541. Note that not all of these are necessarily vulnerable, as specific device versions are not available.
Map of exposed FortiManager instances:
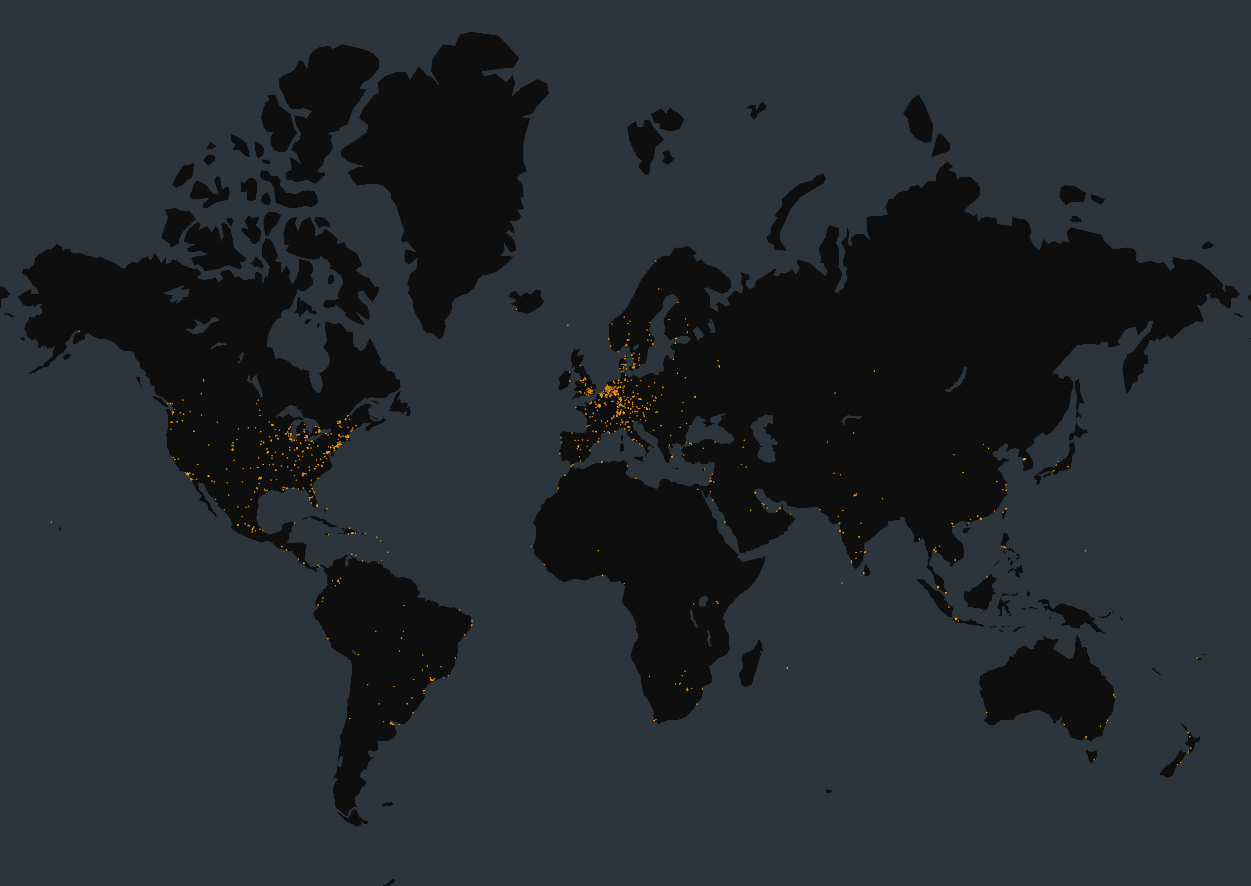
To identify all exposed FortiManager instances on your network regardless of version, the following Censys queries can be used:
services.software: (vendor="Fortinet" and product="FortiManager")
host.services.software: (vendor="Fortinet" and product="FortiManager") or web_entity.instances.software: (vendor="Fortinet" and product="FortiManager")
More details on identifying indicators of compromise can be found in Mandiant’s report.
Additionally, a blog post from Tenable suggests that Shodan identifies ~60,000 FortiManager devices using port 541 and hex signature xAB, but this signature seems to be is lower confidence for identifying FortiManager due to the high probability of producing false positives. The same query performed in Censys Search produces ~375k results:
services: (port=541 and banner_hex:"*ab*")
References
- https://fortiguard.fortinet.com/psirt/FG-IR-24-423
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2024-47575
- https://thehackernews.com/2024/10/fortinet-warns-of-critical.html
- https://cloud.google.com/blog/topics/threat-intelligence/fortimanager-zero-day-exploitation-cve-2024-47575
- https://fortinetweb.s3.amazonaws.com/docs.fortinet.com/v2/attachments/6379fbaa-6dda-11ee-a142-fa163e15d75b/FGFM-7.4-Communications_Protocol_Guide.pdf?ref=labs.watchtowr.com
- https://www.tenable.com/blog/cve-2024-47575-faq-about-fortijump-zero-day-in-fortimanager-fortimanager-cloud




