Summary
- A new hacker group leaked full Fortinet FortiGate firewall configs, including plaintext credentials, for over 15,000 devices from a compromise dating back to 2022
- As of January 17, of the 15,469 distinct compromised hosts, over half are still online and reachable in scans, and 5,086 (32.88%) are still exposing their FortiGate web login interfaces. There have been no major fluctuations in this number since the leak.
- A full list of the affected IPs was shared to GitHub: https://github.com/arsolutioner/fortigate-belsen-leak/blob/main/affected_ips.txt. Check if any of your devices were compromised ASAP.
Context
On January 14, a hacker group known as Belsen leaked configuration data for over 15,000 Fortinet FortiGate firewalls on the dark web for free. The leaked data includes full firewall configurations and plaintext VPN user credentials, organized by country and IP address. The configuration data includes device serial numbers, models, management certs, and more. This is a severe breach given that anyone could leverage this information to infiltrate the compromised networks.
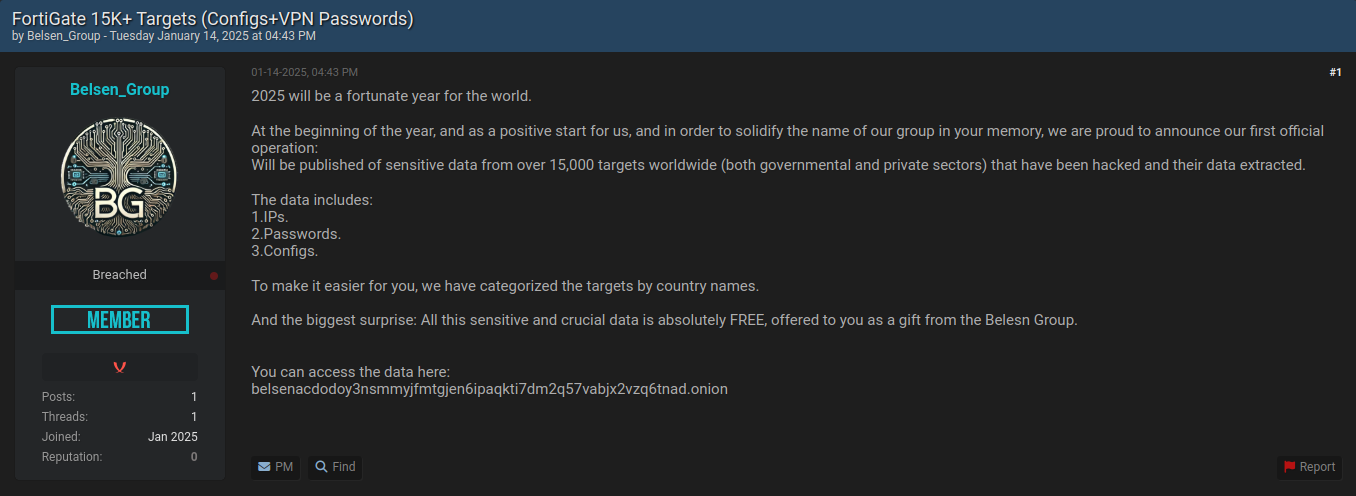
A group dubbed “Belsen_Group” leaked firewall configs and VPN credentials that were apparently obtained in 2022
Researcher Kevin Beaumont conducted an initial analysis of the files and discovered evidence tying these compromises to CVE-2022–40684, an authentication bypass zero-day vulnerability disclosed in October 2022:
“The data appears to have been assembled in October 2022, as a zero-day vuln. For some reason, it has been released today, just over 2 years later.”
Although the data is over two years old, it’s likely still relevant and capable of causing damage. Firewall configuration rules in particular tend to remain unchanged unless a specific security incident prompts an update. It’s also fully possible, of course, that some of these firewalls have changed ownership in the interim, but such cases are also uncommon.
Fortinet, a widely used network security vendor, has faced ongoing scrutiny for its track record of security vulnerabilities, with its FortiGate firewalls frequently targeted in attacks. In fact, on the same day of this recent leak, Fortinet disclosed a new critical authentication bypass zero day (CVE-2024-55591) that is actively being exploited in campaigns targeting FortiGate firewalls, particularly those with admin interfaces publicly exposed to the internet.
A GitHub repository was created with a list of affected IPs to help organizations determine their exposure: https://github.com/arsolutioner/fortigate-belsen-leak/blob/main/affected_ips.txt
The Belsen group itself is new to the scene, having joined the forum only recently on January 3.
To better understand the current level of exposure and potential scope of damage, we enriched the list of compromised IPs using Censys data.
The Scope of Exposure
Out of the 15,469 distinct affected IPs listed in the breach, a Censys scan as of January 17, 2025 found that:
- 8,469 IPs (54.75%) are still online and reachable in scans.
- 5,086 IPs (32.88%) continue to expose the compromised FortiGate login interfaces (primarily on port 443).
While no single country or network dominates the exposure map, Mexico, Thailand, and the U.S. stand out as hosting the largest number of affected devices, with a significant presence also observed on the UniNet network.
The overall potential impact is somewhat mitigated by the fact that about one-third of the leaked IPs are actively exposing their FortiGate firewall web access pages. However that still means over 5,000 hosts are potentially vulnerable.
What Can Be Done?
Check if any of your IPs were compromised: https://github.com/arsolutioner/fortigate-belsen-leak/blob/main/affected_ips.txt
These hosts were reportedly breached back in 2022 via CVE-2022–40684. It’s likely too late to patch against that particular vulnerability if you have been compromised; regardless, update your admin VPN credentials and monitor for unauthorized access.
In addition, it’s strongly recommended to patch against the most recently actively exploited FortiOS zero day, CVE-2024-55591:
| Vulnerable Version |
Patch |
| FortiOS 7.0.0 through 7.0.16 |
Upgrade to 7.0.17 or above |
| FortiProxy 7.2.0 through 7.2.12 |
Upgrade to 7.2.13 or above |
| FortiProxy 7.0.0 through 7.0.19 |
Upgrade to 7.0.20 or above |
References: