On January 30th, 2023, information emerged about a new vulnerability that targets QNAP devices. Although there is little information about the vulnerability details, we know that it affects QNAP QTS devices running versions less than 5.0.1.2234 and QuTS Hero versions less than “h5.0.1.2248” and was fixed with QTS version 5.0.1.2234 and QuTS Hero h5.0.1.2248. This is currently tracked as CVE-2022-27596.
We also know that if the exploitation is successful, an attacker can “inject malicious code”; QNAP has deemed this a critical vulnerability with a low attack complexity, no authentication required, and it can be exploited remotely. We also know that the Common Weakness Enumerator (CWE) it was assigned is “CWE-89”: Improper Neutralization of Special Elements used in an SQL Command (or SQL injection).
What we know right now:
- It is a SQL injection vulnerability
- Trivial to exploit
- It does not require authentication
We’ve discussed problems with QNAP regarding the Deadbolt Ransomware campaigns, which at their height had infected over 20,000 devices and successfully stolen just under $200,000 from victims. And while there are no indications that bad actors are using this new exploit, the threat is definitely on the horizon.
Given that the Deadbolt ransomware is geared to target QNAP NAS devices specifically, it’s very likely that if an exploit is made public, the same criminals will use it to spread the same ransomware again.
Censys has observed 67,415 hosts with indications of running a QNAP-based system; unfortunately, we could only obtain the version number from 30,520 hosts. But, if the advisory is correct, over 98% of identified QNAP devices would be vulnerable to this attack. We found that of the 30,520 hosts with a version, only 557 were running QuTS Hero greater than or equal to “h5.0.1.2248” or QTS greater than or equal to “5.0.1.2234”, meaning 29,968 hosts could be affected by this vulnerability.
If the exploit is published and weaponized, it could spell trouble to thousands of QNAP users. Everyone must upgrade their QNAP devices immediately to be safe from future ransomware campaigns.
Top Ten Countries
Below is a summary of the top ten countries with hosts running versions of QNAP that are deemed vulnerable to CVE-2022-27596. Most of these hosts reside in the United States (3,271 total, 3,149 vulnerable) and Italy (3,239 total, 3,200 vulnerable).
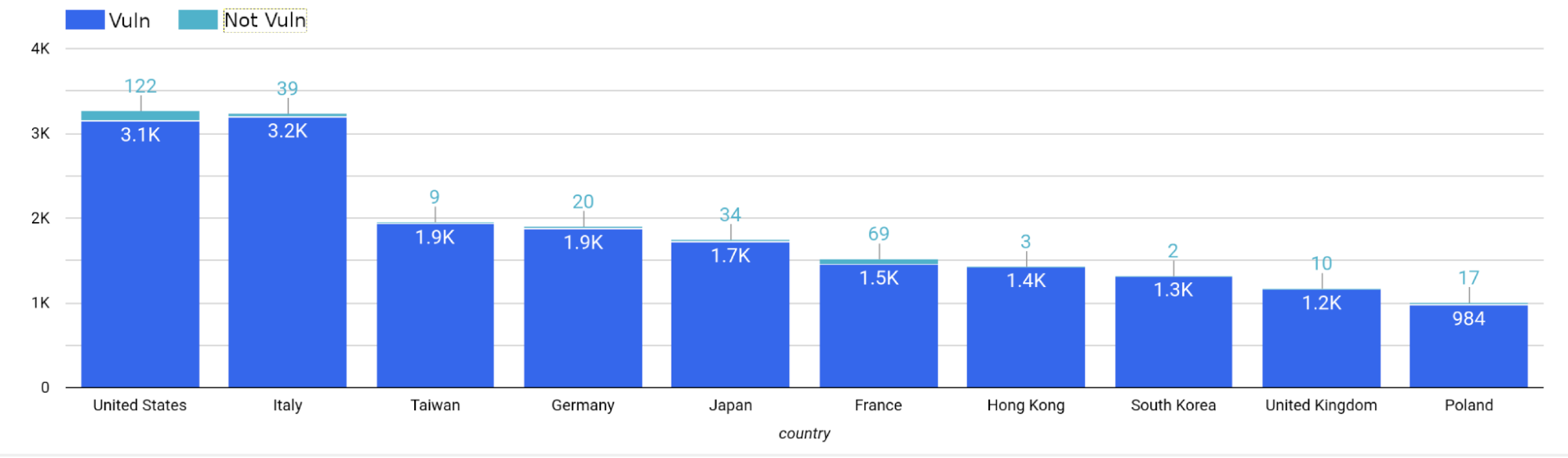 |
| Country |
Total Hosts |
Non-Vulnerable Hosts |
Vulnerable Hosts |
| United States |
3,271 |
122 |
3,149 |
| Italy |
3,239 |
39 |
3,200 |
| Taiwan |
1,951 |
9 |
1,942 |
| Germany |
1,901 |
20 |
1,881 |
| Japan |
1,748 |
34 |
1,714 |
| France |
1,527 |
69 |
1,458 |
| Hong Kong |
1,425 |
3 |
1,422 |
| South Korea |
1,313 |
2 |
1,311 |
| United Kingdom |
1,167 |
10 |
1,157 |
| Poland |
1,001 |
17 |
984 |
|